Cash Ratio: Definition, Formula, and Example
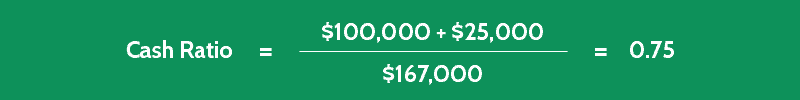
Assets America was responsible for arranging financing for two of my multi million dollar commercial projects. At the time of financing, it was extremely difficult to obtain bank financing for commercial real estate. Not only was Assets America successful, they were able expansion and contraction of demand are referred to as the to obtain an interest rate lower than going rates. The company is very capable, I would recommend Assets America to any company requiring commercial financing. In the largest sense, the current CCR tells us whether you are running a profitable business or a stinker.
Apply For Financing
- This indicates how well a company can cover its short-term debts with its liquid assets and indicates how much leverage the company may have over other creditors.
- Specifically, these include remodeling the place and installing newer cooking equipment.
- This ratio is particularly useful in industries where cash flow stability is key, such as utilities, telecommunications, or any business with predictable cash flows.
- Obviously, if you cannot earn enough income each month to pay your bills, then you have a major problem.
- The calculation of a company’s current cash debt coverage ratio aids lenders in assessing the company’s capability to repay debts.
Business owners should aim for a ratio of 2 or above, which means that interest expenses can be covered two times over. An interest coverage ratio of two or higher is generally considered satisfactory. Amanda Bellucco-Chatham is an editor, writer, and fact-checker with years of experience researching personal finance topics.
Calculation Examples
It’s not realistic for a company to maintain excessive levels of cash and near-cash assets to cover current liabilities. The cash ratio is generally a more conservative look at a company’s ability to cover its debts and obligations compared to other liquidity ratios. It sticks strictly to cash or cash-equivalent holdings, leaving other assets such as accounts receivable out of the equation. The current cash debt coverage ratio is a liquidity ratio that measures the efficiency of an entity’s cash management. This ratio determines the company’s position to pay off its entire debt from its earnings. This ratio measures the company’s ability to repay the entire principal plus interest obligation of debt in the near term.
Do you own a business?
These ratios (including profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, solvency ratios, and activity ratios) act as a metric to assess the entity’s financial performance. It is because its debt has increased over the years, and EBIT has gone down. It happened because of the margin pressure and the entry of Reliance Jio into the market.
Examples of Coverage Ratios
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
Verified Metrics Achieves SOC 2 Type 1 Certification

Specifically, these include remodeling the place and installing newer cooking equipment. Therefore, the restaurant owner visits its local bank seeking a $500,000 loan. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
A company’s earnings before interest, taxes, and non-cash expenses are available in the income statement. There may be a number of additional non-cash items to subtract in the numerator of the formula. For example, there may have been substantial charges in a period to increase reserves for sales allowances, product returns, bad debts, or inventory obsolescence. If these non-cash items are substantial, be sure to include them in the calculation. A company may be inefficient in managing cash and leveraging low credit terms.
The above formula uses a company’s total cash instead of earnings before interest and taxes. Similarly, it does not require companies to include non-cash expenses in the calculation. Although the interest expenses may include accrued interest, it is still crucial for companies to own resources to cover them. Usually, stakeholders prefer the cash coverage ratio to be significantly higher than 1. It is similar to the interest coverage ratio, which examines whether companies can repay the interest expense. The cash coverage ratio focuses on whether companies have enough cash resources to cover interest payments.
If this continues in the future, Bharti Airtel could be in a bad position. As a result of this, it has to sell off its assets to repay the loan. It can be used to conduct trend analysis for a company over a period. This calculation shows how its debt-repaying ability is moving over the periods. If it is going down, the firm can have a look at the issue and it can try to rectify that.
A coverage ratio is a financial ratio used to measure a company’s ability to repay financial obligations. Several coverage ratios look at how companies can cover those obligations. A cash ratio equal to or greater than one generally indicates that a company has enough cash and cash equivalents to entirely pay off all short-term debts. A ratio under 0.5 is considered risky because the entity has twice as much short-term debt compared to cash.
Some brands may utilize the cash coverage ratio to attract investors. This ratio may also determine the company’s financial requirements, which can be useful when approaching investors. More investors may be ready to invest if the firm can demonstrate that it can service its debt. Common coverage ratios include the interest coverage ratio, debt service coverage ratio, and asset coverage ratio. These are short-term debt instruments that you can quickly convert to cash. They include Treasury bills, money market funds, commercial paper, short-term government bonds and marketable securities.



















You must be logged in to post a comment.